
- MYSQL WORKBENCH EXPORT DATABASE HOW TO
- MYSQL WORKBENCH EXPORT DATABASE PRO
- MYSQL WORKBENCH EXPORT DATABASE PROFESSIONAL
Anyway as I had to do it for my grades I had to look for this up on the internet and took me some time to get how to do it properly even tho I thought I knew how to use MySQL Workbench.So I am writing this just in case you are looking for it for the first time.
MYSQL WORKBENCH EXPORT DATABASE PROFESSIONAL
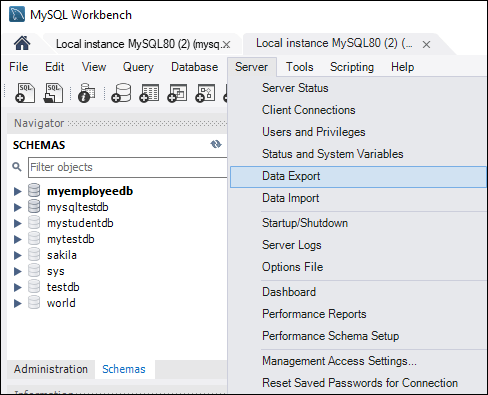
As I knew MySQL syntax before I preferred to make my project in MySQL and as I am primarily a Windows user I am writing my SQL scripts in MySQL workbench.But it took me by surprise when our teacher asked us to send him only one SQL script which has everything he asked for in the first place.So to describe it a bit more I had to send him only one SQL script when executed it should create the database at the first place then the tables, views,stored procedures and functions as well.I was a little bit surprised because usually in the professional work environment you are supposed to make them in separate scripts and put them under source control so that your teammates can also work on it without messing up with the data inside. So, as I took a database course at my university this semester and our teacher asked us to go for SQL first then learning NoSQL databases such as MongoDB.After the first half of the course, we had to create&design a whole working database in SQL and present it to the teacher as a project. Your database is ready to use.Hello there devs! I hope you guys are doing well and staying safe in this pandemic. The form editor is just as easy to use you only need to remember to click the Next Entry button (single right-pointing arrow) to move to the next data row ( Figure F), before entering new data.Ĭongratulations, you successfully created a database, added a table, and entered data into the table. Once you add all of your data, click Apply to execute the SQL Script. Double-click under that newly created row and create another. After entering the necessary data, hit Enter on your keyboard. Double-click the first entry in one of your columns and type the data to be added. For the fastest route to success, use the result grid (which is the default). In this window, you can either use the result grid or open the form editor. You will then find yourself in a window that allows you to enter data ( Figure E). In order to start adding data to a table, right-click the table (in the SCHEMAS pane) to be modified and click Select Rows. In previous incarnations of MySQL Workbench, a button could be found on the home screen that took you directly to the table data entry section. It’s now time to populate that table with some data. Once you do that, you can then select the Datatype for the column ( Figure D).Ĭontinue adding columns until your table is complete. In the new window ( Figure C), name the table.ĭouble-click under Column Name, and you should be able to type the name of the first column. Expand that listing, right-click the Tables entry, and select Create Table. I’ve created a database called SERVERS, that will be listed in the SCHEMAS pane. Once the schema is created, close the SQL Script window. Once you name your schema, click the Apply button and, when prompted, review the SQL Script and click Apply again. In the resulting window ( Figure B), give the schema (database) a name and (if necessary) select a Default Collation. From the database home screen ( Figure A), right-click a blank spot under the SCHEMAS pane and select Create Schema. Open MySQL Workbench and connect to your database server. The first thing to do is create a database (aka Schema). I will assume you already have MySQL Workbench installed. You need to make sure you have MySQL set up for remote connections ( See: How to set up MySQL for remote access on Ubuntu Server 16.04 (This also works for Ubuntu 18.04).

My instance of MySQL Workbench will connect to a MySQL database, housed on Ubuntu Server 18.04. I’ll use MySQL Working 6.3, which has drastically evolved from older versions of the tool.
MYSQL WORKBENCH EXPORT DATABASE PRO
SEE: Server deployment/migration checklist (Tech Pro Research) What you need To do so, I’ll walk you through the process of creating a database, adding a table to that database, and then adding data to the table. I’m going to show you just how easy it is to make use of MySQL Workbench. Kubernetes is the key to cloud, but cost containment is criticalĪzure Monitor’s Change Analysis helps you troubleshoot problems quickly Networking: Must-read coverageĥG Open RAN gains momentum: Next steps and challenges It’s cross-platform, open source, and incredibly easy to use. This particular tool is one of the finest locally installed MySQL client tools you’ll find. Fortunately, for those users, there are plenty of GUIs available to make the task easier. To others, however, the command line is too cumbersome to be efficient. To them, it’s as efficient as a work environment can be. Many database administrators are comfortable working within the command line.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
